How Credit Card helps generating profits ?
How Banks make Money through Credit Cards?
SHUCHI.P.NAHAR
To understand how credit
cards works, which customer segments it serves, what it offers to its customer
segments, and how does it makes money from them, we need to get familiar with
few terms. Credit cards classifies the banks as either Issuers or Acquirers.
Issuers issue cards to the cardholders, whereas the Acquirers manage the
relationship with the merchants.
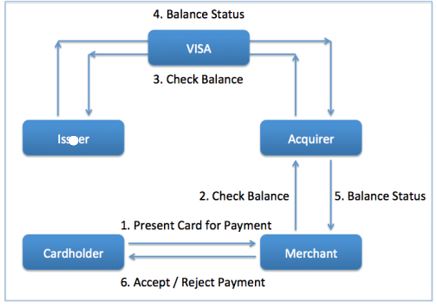
The diagram below explains
what happens behind-the-scenes when a cardholder presents a card for payment to
a merchant.
What types of risk bank
accepts?
Bank usually accepts three
types of risk
1) Credit
2)Liquidity
3)Interest rate and they get paid to take on the risk.
1) Credit
2)Liquidity
3)Interest rate and they get paid to take on the risk.
Managing credit risk
Credit risk is the core
part of the lending business . investors can get a sense of a banks credit
quality by examining its balance sheet , loan categories , trends in non
performing loans and charge off rates as well as managements lending philosophy.
When a cardholder presents
a card for payment to a merchant, the payment request is forwarded to the
acquirer. The acquirer contacts the issuer through the VISA network. The issuer
shares the information on whether sufficient balance is available to carry out
the transaction.
The information is then routed to the merchant. In case sufficient balance is available, the payment is accepted. Else, it is rejected. The issuer bills the cardholder on a monthly basis. The cardholder pays those bills then.
The information is then routed to the merchant. In case sufficient balance is available, the payment is accepted. Else, it is rejected. The issuer bills the cardholder on a monthly basis. The cardholder pays those bills then.
What is ignored in the diagram the reality is explained below!
What the above diagram does not tell
is how VISA and banks make money in the process. They make money from the
transaction fees charged to merchants. To understand how it works, imagine a
$100 payment from a cardholder to merchant.
In case the merchant fee is 2.4%, the merchant would get $97.60 from the transaction. $2.40 would get unevenly split between issuer and acquirer, depending upon the interchange fee. In case of an interchange rate of 1.8%, the issuer will keep $1.80 and acquirer will keep $0.60.
Issuer gets to keep more of the merchant fee because of a higher risk of payment default from the cardholder.
In case the merchant fee is 2.4%, the merchant would get $97.60 from the transaction. $2.40 would get unevenly split between issuer and acquirer, depending upon the interchange fee. In case of an interchange rate of 1.8%, the issuer will keep $1.80 and acquirer will keep $0.60.
Issuer gets to keep more of the merchant fee because of a higher risk of payment default from the cardholder.
VISA makes money on payment volumes,
transaction processing, and value-added services.
How individual makes money out of this process is explained below:
VISA creates value for all
its stakeholders during the process. Cardholders’ benefit because of convenience,
security, and rewards associated with card payments.
Merchants benefit from
improved sales by offering payment method options to the customers. Banks get
new revenue streams through card fees, late payment interests, and transaction
fee cuts.
Chart explaining the business model for banking companies
Chart explaining the business model for banking companies
Income from Credit Card Interest and Merchant Fees
The primary way that banks make money is interest from credit
card accounts. When a cardholder fails to repay their entire balance in a given
month, interest fees are charged to the account. For any given account, the
interest charged is equal to the card's periodic rate multiplied by the average
daily balance and number of days in a billing period. The periodic rate is the
annual percentage rate (APR) divided by 365. In the United States, the average
credit card interest rate paid by interest-bearing accounts is 14.87%.
The second largest source of income for credit card companies
are fees collected from merchants. When a retailer accepts a credit card
payment, a percentage of the sale goes to the card's issuing bank. This is
commonly referred to as the interchange rate. In the US, the average
interchange rate is around 1.75%, though it varies from card to card and
retailer to retailer.
Credit card companies make money by collecting fees. Out of the
various fees, interest charges are the primary source of revenue. When credit
card users fail to pay off their bill at the end of the month, the bank is
allowed to charge interest on the borrowed amount. Other fees, such as annual fees
and late fees, also contribute, though to a lesser extent. Another major source
of income for credit card companies are fees collected from merchants who
accept card payments. These average out to approximately 1.75% of each
transaction. Through the fees they get to collect, banks make a profit on their
credit card business—approximately 4.04% of quarterly assets.
How Credit Card Companies Make Money or Earn Profit
1. Marketing Tie-ups
You know who is making money these days? Anyone who helps
brand/companies extend their reach. With each passing day, it is difficult to
generate business. You may check the financial results of the company. For
example, brands are spending more on digital marketing because of its reach.
The credit card companies have direct access to their customer base and can
influence their spending. Therefore, credit card companies can help in both i.e
brand promotion and to generate sales. It is very effective and potent tool to
reach new customers. In other words, the objective is to increase sale. These
tie-ups are in the form of freebies, cashback offers, EMI offers etc. Knowingly
or unknowingly customer end up spending more on the credit cards. As per RBI
data, HDFC Bank has issued 62.8L credit cards followed by ICICI Bank at 35L
credit cards. SBI, Citibank, and Axis Bank are at no 3, 4 and 5 respectively.
2. Interest on Balance Outstanding
It’s a universal fact that interest rate on a credit card is
highest among all forms of credit facilities even higher than private lending.
It can be as high as 42% (annually) or 3.5% (monthly). According to industry
estimates, more than 50% of the credit card balance outstanding is not paid on
time. These customers are GOD for credit card companies. Let me clarify that it
is not necessary that 50% credit card balance outstanding means 50% customers are defaulting/delaying the payment.
The
amount should be considered in absolute terms only. I don’t want to make this
post data heavy. Assuming everything remains equal. In this case, credit card
companies are receiving half the payment (absolute) on time and there is a delay
in balance half payment. Therefore for delayed payment credit card companies
are charging 42% interest rate.
To simplify, we can safely assume that credit
card companies are earning interest of 21% of the total outstanding balance. In
other words, the amount spent on a credit card by the customers is fetching an
interest of 21% to banks. From which line of credit, the bank can generate
interest income of 21%. Even if you adjust settlements and written off amount,
my guess is that net interest income should be 18% or more.
3. Cash Advance Charges
The credit card users are aware that they can withdraw cash
against credit card limit. Normally cash limit is 40% of credit limit. This
cash limit can come handy in case of any emergency cash requirement as a short
term loan.
For example, if my credit limit is Rs 5L then i can withdraw a cash
of Rs 2L from my credit card account. I have to bear transaction fees of 2.5%
(Min Rs 300). Therefore, if i withdraw 2L then i will be charged transaction
fees of Rs 5,000. Besides transaction charges, the bank also charges an
interest rate of up to 42% (annually) i.e. 3.5% p.m. from the date of
withdrawal until the date of full payment.
This is one of the costliest loan
option and a most profitable option for the bank to lend during an emergency to
the customer.
4. Annual and Renewal Fees
This is normally paid by the customers whose credit card spend
is low. In other words, credit card companies charge annual/renewal fees in
case customer is using credit card below the threshold limit set by the bank.
It helps to recover the cost of providing the service to low usage customers.
5. Miscellaneous Charges
Besides this, credit card companies
also charge some miscellaneous charges like
(a) Late Payment Charges
(b) Charges on over limit. Normally 2.5%.
(c) Payment return charges
(d) Reward redemption fee
(e) Cash processing fee
(f) Reissue of card.
(a) Late Payment Charges
(b) Charges on over limit. Normally 2.5%.
(c) Payment return charges
(d) Reward redemption fee
(e) Cash processing fee
(f) Reissue of card.
Sources: Nerdwallet.com
Valuepenguin.com
Nitinbhatia's Report
Investopedia






Comments
Post a Comment